By John Patzakis and Brent Botta
In recent posts, we have addressed the issue of evidentiary authentication of social media data. (See previous entries here and here). General Internet site data available through standard web browsing, instead of social media data provided by APIs or user credentials, presents slightly different but just as compelling challenges.
The Internet provides torrential amounts of evidence potentially relevant to litigation matters, with courts routinely facing proffers of data preserved from various websites. This evidence must be authenticated in all cases, and the authentication standard is no different for website data or chat room evidence than for any other. Under Federal Rule of Evidence 901(a), “The requirement of authentication … is satisfied by evidence sufficient to support a finding that the matter in question is what its proponent claims.” United States v. Simpson, 152 F.3d 1241, 1249 (10th Cir. 1998).
Ideally, a proponent of the evidence can rely on uncontroverted direct testimony from the creator of the web page in question. In many cases, however, that option is not available. In such situations, the testimony of the viewer/collector of the Internet evidence “in combination with circumstantial indicia of authenticity (such as the dates and web addresses), would support a finding” that the website documents are what the proponent asserts. Perfect 10, Inc. v. Cybernet Ventures, Inc. (C.D.Cal.2002) 213 F.Supp.2d 1146, 1154. (emphasis added) (See also, Lorraine v. Markel American Insurance Company, 241 F.R.D. 534, 546 (D.Md. May 4, 2007) (citing Perfect 10, and referencing MD5 hash values as an additional element of potential “circumstantial indicia” for authentication of electronic evidence).
One of the many benefits of X1 Social Discovery is its ability to preserve and display all the available “circumstantial indicia” – to borrow the Perfect 10 court’s term — to the user in order to present the best case possible for the authenticity of Internet-based evidence collected with the software. This includes collecting all available metadata and generating a MD5 checksum or “hash value” of the preserved data.
But html web pages pose unique authentication challenges and merely generating an MD5 checksum of the entire web page, or just the web page source file, provides limited value because web pages are constantly changing due to their very fluid and dynamic nature. In fact, a web page collected from the Internet in immediate succession would very likely calculate two different MD5 checksums. This is because web pages typically feature links to many external items that are dynamically loaded upon each page view. These external links take the form of cascading style sheets (CSS), graphical images, JavaScripts and other supporting files. This linked content can be stored on another server in the same domain, but is often located somewhere else on the Internet.
When the Web browser loads a web page, it consolidates all these items into one viewable page for the user. Since the Web page source file contains only the links to the files to be loaded, the MD5 checksum of the source file can remain unchanged even if the content of the linked files become completely different. Therefore, the content of the linked items must be considered in the authenticity of the Web page. X1 Social Discovery addresses these challenges by first generating an MD5 checksum log representing each item that constitutes the Web page, including the main Web page’s source. Then an MD5 representing the content of all the items contained within the web page is generated and preserved.
To further complicate Web collections, entire sections of a Web page are often not visible to the viewer. These hidden areas serve various purposes, including metatagging for Internet search engine optimization. The servers that host Websites can either store static Web pages or dynamically created pages that usually change each time a user visits the Website, even though the actual content may appear unchanged.
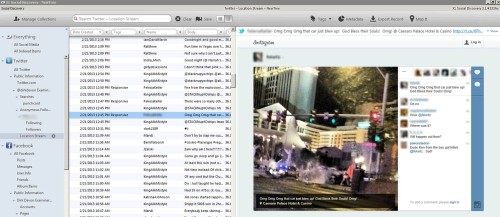
In order to address this additional challenge, X1 Social Discovery utilizes two different MD5 fields for each item that makes a Web page. The first is the acquisition hash that is from the actual collected information. The second is the content hash. The content hash is based on the actual “BODY” of a Web page and ignores the hidden metadata. By taking this approach, the content hash will show if the user viewable content has actually changed, not just a hidden metadata tag provided by the server. To illustrate, below is a screenshot from the metadata view of X1 Social Discovery for website capture evidence, reflecting the generation of MD5 checksums for individual objects on a single webpage:
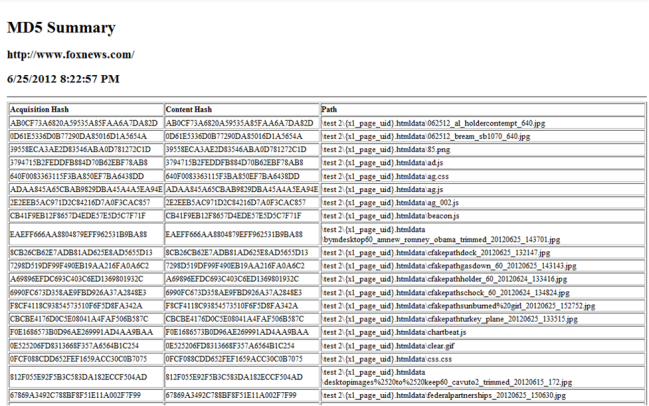
The time stamp of the capture and url of the web page is also documented in the case. By generating hash values of all individual objects within the web page, the examiner is better able to pinpoint any changes that may have occurred in subsequent captures. Additionally, if there is specific item appearing on the web page, such as an incriminating image, then is it is important to have an individual MD5 checksum of that key piece of evidence. Finally, any document file found on a captured web page, such as a pdf, Powerpoint, or Word document, will also be individually collected by X1 Social Discovery with corresponding acquisition and content hash values generated.
We believe this approach to authentication of website evidence is unique in its detail and presents a new standard. This authentication process supports the equally innovative automated and integrated web collection capabilities of X1 Social Discovery, which is the only solution of its kind to collect website evidence both through a one-off capture or full crawling, including on a scheduled basis, and have that information instantly reviewable in native file format through a federated search that includes multiple pieces of social media and website evidence in a single case. In all, X1 Social Discovery is a powerful solution to effectively collect from social media and general websites across the web for both relevant content and all available “circumstantial indicia.”