The Sedona Conference® has published for public comment a key document: The Sedona Conference® Primer on Social Media. Sedona is a highly influential organization so this is an important development further underscoring the importance of social media evidence. According to Sedona, the Primer “provides best practice guidance on the corporate use and management of social media, as well as their preservation, collection, and production in the form of electronically stored information (ESI).”
The Sedona Conference® has published for public comment a key document: The Sedona Conference® Primer on Social Media. Sedona is a highly influential organization so this is an important development further underscoring the importance of social media evidence. According to Sedona, the Primer “provides best practice guidance on the corporate use and management of social media, as well as their preservation, collection, and production in the form of electronically stored information (ESI).”
The document is publicly available for download here.
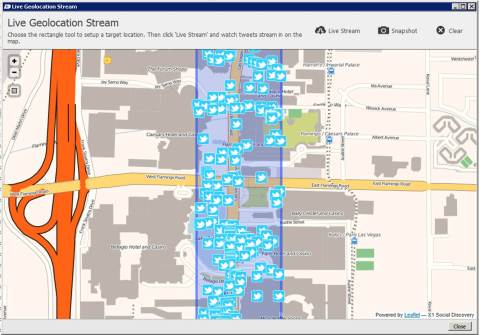
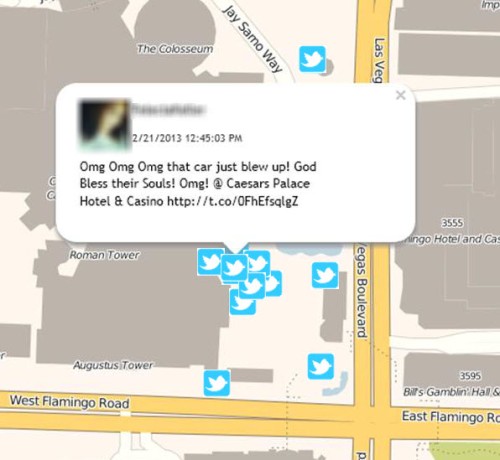
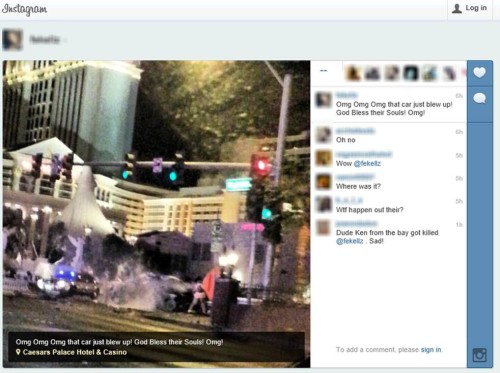
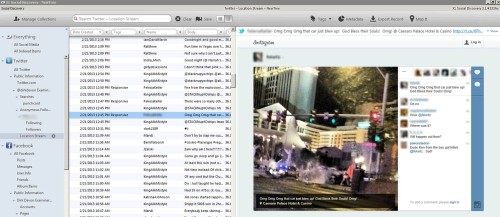
The Primer is a good read and the section II in particular highlights the discoverability of social media, its importance and necessity for best practices technologies such as X1 Social Discovery.
I have extrapolated some of the key quotes, adding headings to segment them by subject, with my comments to some in italics:
On the Scope of Social Media Usage:
“Hundreds of millions of individuals now use social media to communicate and to build online communities…Social media is also increasingly important for business organizations and the legal community—the former largely because of their marketing potential, and the latter as yet another source of information to be regulated, managed, and ultimately preserved and produced during investigations or litigation. Twenty-two percent of Fortune 500 companies now have a public-facing blog that has received at least one post in the last 12 months.”
-Page 1
On the Court’s Increasing Trend to allow Liberal Discovery of Social Media:
“As the case law continues to develop in the area of social media and privacy, the trend appears to be that courts will not recognize or protect privacy interests of those who voluntarily engage in social media communications. Although initial cases addressing this issue arise in the context of labor and employment, family law, and personal injury matters, where unique considerations broadly implicate the sort of information found on social media sites, the opinions indicate that, in the future, social media and privacy could likely become mutually exclusive concepts in the law.”
-Page 22
“Various courts have already found that social media content that is relevant to litigation is discoverable. For example, one court found that social media might be relevant to understanding the emotion, feeling, or mental state of claimants in a sexual harassment suit. And sanctions are possible for spoliation of social media content, as with any sort of relevant information. Thus, it is clear that social media content that is relevant to reasonably anticipated litigation must be preserved.”
-Page 34
On Defensibility of Collection and Preservation Processes:
“simply printing out social media site data could result in an incomplete and inaccurate data capture that is hard to authenticate…Also, social media sites can contain data and information, such as video content, that cannot be properly collected in the form of static images (i.e., screen shots and .pdf images).”
-Page 38
Comment: This is a key point emphasized many times on this blog. Screenshots are not only questionable in terms of defensibility and incompleteness, but also prevent any scalable investigation process.
“Third-party providers are developing solutions that go beyond capturing static and single point in-time images from a specific social media site, and instead allow certain content to be downloaded or collected in a way that better preserves the content and captures the unique metadata fields associated with social media data. Properly captured, these metadata fields can assist with establishing the chain of custody and with authentication, and help to facilitate more accurate and efficient data processing and review. Currently, the full range of metadata associated with social media data can only be collected with specialized e-discovery software designed for that purpose.”
-Page 39
Comment: We could not have said this better. Sedona is essentially describing X1 Social Discovery, in our opinion.
“Social media sites can, and some do, publish rules and specifications that allow application programming interfaces (APIs) to interact with the social media site in order to capture social media site data by automated means. Because these products integrate with the APIs published by the providers, they are better able to filter data and collect social media data in a more defensible manner, including by collecting all available metadata fields for individual social media items and by generating MD5 hash values for collected social media items. The products are multiplying rapidly and undergoing refinement, spurred on by the need to fill the new regulatory niche, with flow-on effects for e-discovery. When properly developed, these products are registered and approved by the provider and their use is subject to specific terms of service for developers.”
-Page 39
Comment: Again, we could not have said this better. Only software specifically designed to collect social media evidence for judicial purposes can collect social media evidence in a manner consistent with the functionality described by Sedona.